
- INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT HOW TO
- INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT MAC OS
- INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT INSTALL
- INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT FULL
So, have you ever wanted to have a single USB drive with multiple bootable Linux distros? How did you manage it? Also, if you know of any other methods to create a bootable Live USB with multiple Linux based operating systems, do let us know about them in the comments section below. However, be careful that you allow each of the operating systems at least 4-8 GB of space on the USB drive, to ensure that they can run smoothly.
INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT INSTALL
Now that you know how you can install multiple Linux distros on the same USB drive, and boot into any one of them, feel free to use YUMI to install as many Linux distros on your USB flash drive. SEE ALSO: 10 Must Have Linux Apps You Should Install Easily Create Multiboot Linux USB with YUMI You can use this method to use YUMI on a Mac. I haven’t tried it on any Linux distro, but the process of running YUMI on Linux using Wine should be similar to running YUMI on Mac. YUMI will immediately launch on your Mac, and you can follow the steps given in the previous section to install multiple Linux distros on your USB drive.
/dual-boot-linux-and-mac-os-4125733-e14f9fd4e70f4577a4ff4fb7a2ac9e56.jpg)
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info.3. # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk/'. It is easy to install Ubuntu on Windows 10 I hope you found this Itechguide helpful. For the detailed steps to complete this task, click this link Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows 10. # Created by anaconda on Tue Dec 17 03:28:04 2019 The final step to install Ubuntu on Windows 10 by dual-booting both operating systems is to install Ubuntu. It happens mostly when you have a remote filesystem. In my case, I want to edit the tekneed filesystems that are preventing my system from booting by commenting it out (#).
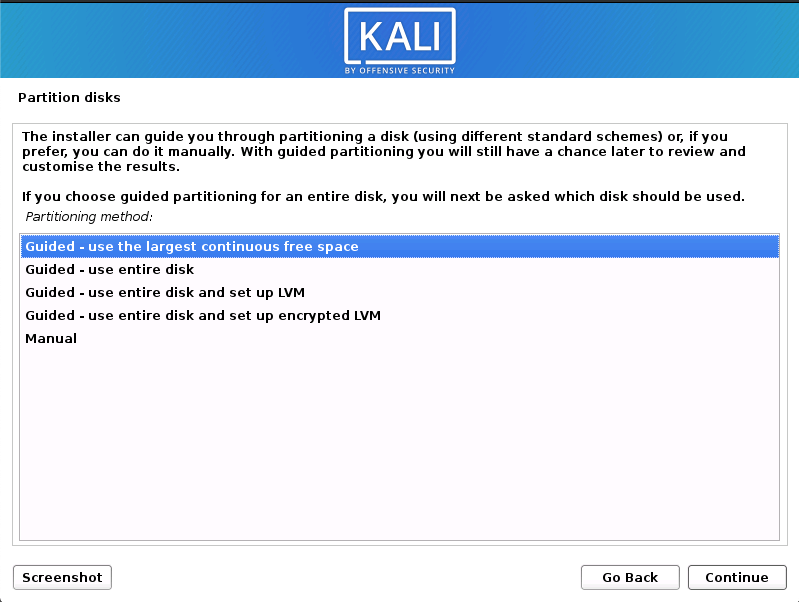
mount the real rootfilesystem depending on the way you boot to single user mode # chroot /sysroot 3. boot into single usermode as done above 2. Some filesystems defined in the fstab can prevent the system from booting, to make changes to fstab, do the following. To be able to perform some tasks and make some changes, the root filesystem is required to be mounted on “/”, hence it will require the use of chroot tool to be able to mount the root filesystem on “/” logically. If necessary, using OS Xs Disk Utility, adjust the sizes of your partitions, making room for Linux.
INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT MAC OS
More so, using some of these methods will make the root filesystem to be mounted on /sysroot. To install Ubuntu Linux 12.04 on an Intel-based Mac, follow these directions: If necessary, install Mac OS X. To be able to make any changes, the root filesystem permission needs to be changed to read-write (rw). Going forward, with these methods we are going to use in the “ ACTION TIME” section, the root filesystem, after being mounted will have a read only (ro) permission. This mode is basically used for maintenance like we earlier said, and troubleshooting such as, resetting a lost root password, repairing bad filesystems (fsck), editing the fstab file to make the system boot properly, stopping services disrupting the system from booting, etc

INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT FULL
In single user mode, the system is booted to a minimal environment with filesystems(local filesystems) being mounted, but without network services, the full operating system is not functional in this mode and most services will be manually started.
INSTALL LINUX ON A MAC SINGLE BOOT HOW TO
In this subject matter, we will look at how to boot into a single user mode (runlevel 1) without the imputing the root password. However, both methods will require the input of the root password. In one of the articles on this site, I discussed how a system runlevel/runtarget can be changed from an operational/command mode and how it can also be changed from the boot menu. Single user mode is also referred to as runlevel 1 and can be called emergency or maintenance mode.īooting in this mode can be done in many ways. From the word single, single user mode is the mode in a Linux system where only one user, the root is allowed to perform system tasks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
